{"value":"With [Amazon Redshift](https://aws.amazon.com/redshift/), you can analyze data in the cloud at any scale. Amazon Redshift offers native data protection capabilities to protect your data using automatic and manual snapshots. This works great by itself, but when you’re using other Amazon Web Services services, you have to configure more than one tool to manage your data protection policies.\n\nTo make this easier, I am happy to share that we added support for Amazon Redshift in [Amazon Web Services Backup](https://aws.amazon.com/backup/). Amazon Web Services Backup allows you to define a central backup policy to manage data protection of your applications and can now also protect your Amazon Redshift clusters. In this way, you have a consistent experience when managing data protection across all supported services. If you have a multi-account setup, the centralized policies in Amazon Web Services Backup let you define your data protection policies across all your accounts within your[ Amazon Web Services Organizations](https://aws.amazon.com/organizations/). To help you meet your regulatory compliance needs, Amazon Web Services Backup now includes Amazon Redshift in its [auditor-ready reports](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-backup/latest/devguide/aws-backup-audit-manager.html). You also have the option to use [Amazon Web Services Backup Vault Lock](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-backup/latest/devguide/vault-lock.html) to have immutable backups and prevent malicious or inadvertent changes.\n\nLet’s see how this works in practice.\n\n**++Using Amazon Web Services Backup with Amazon Redshift++**\nThe first step is to turn on the **Redshift** resource type for Amazon Web Services Backup. In the[ Amazon Web Services Backup console](https://console.aws.amazon.com/backup), I choose **Settings **in the navigation pane and then, in the **Service opt-in** section,** Configure resources**. There, I toggle the **Redshift** resource type on and choose **Confirm**.\n\n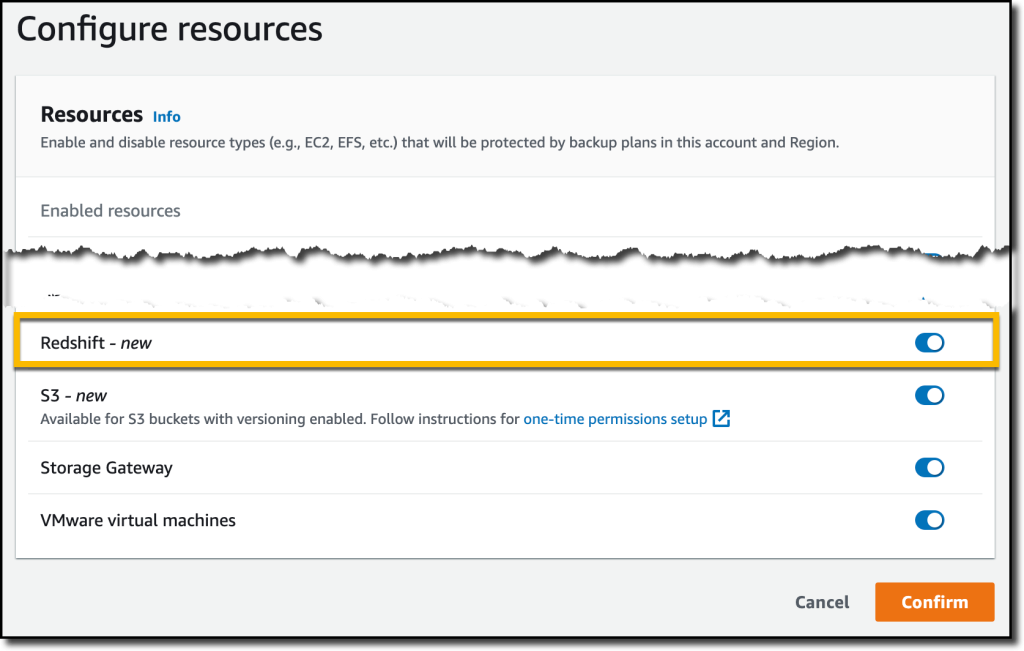\n\nNow, I can create or update a **backup plan** to include the backup of all, or some, of my Redshift clusters. In the backup plan, I can define how often these backups should be taken and for how long they should be kept. For example, I can have daily backups with one week of **retention**, weekly backups with one month of retention, and monthly backups with one year of retention.\n\nI can also create on-demand backups. Let’s see this with more details. I choose **Protected resources** in the navigation pane and then **Create on-demand backup**.\n\nI select **Redshift** in the **Resource type** dropdown. In the Cluster identifier, I select one of my clusters. For this workload, I need two weeks of retention. Then, I choose **Create on-demand backup**.\n\n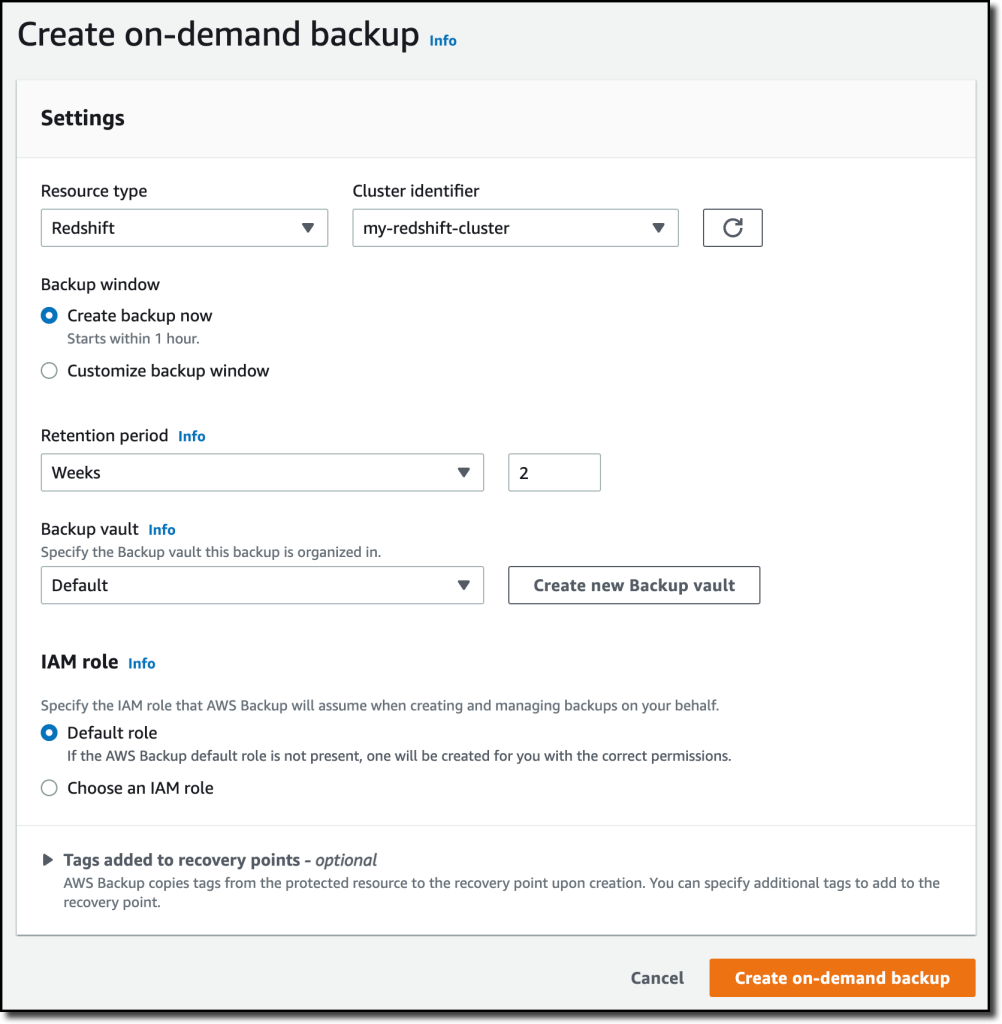\n\nMy data warehouse is not huge, so after a few minutes, the backup job has completed.\n\n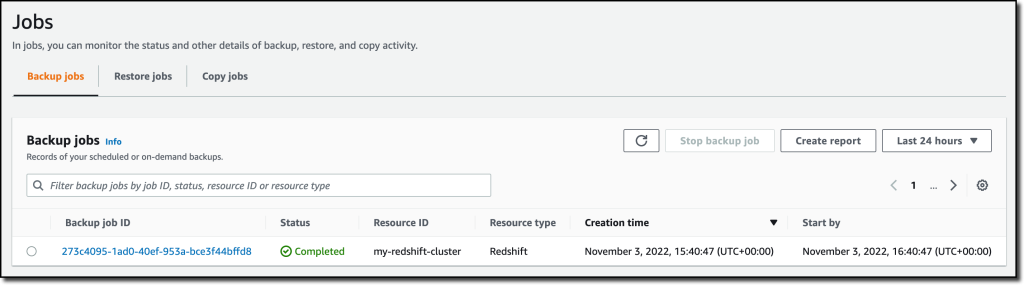\n\nI now see my Redshift cluster in the list of the resources protected by Amazon Web Services Backup.\n\n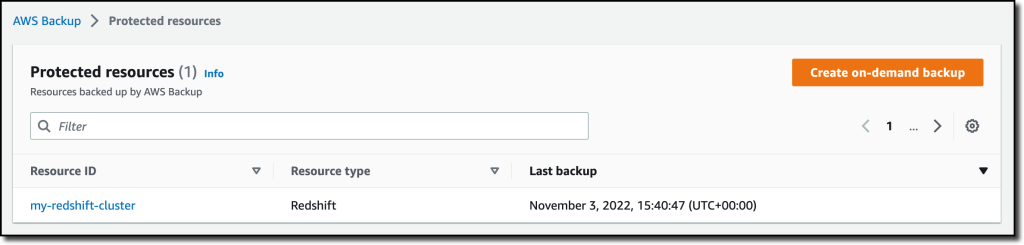\n\nIn the **Protected resources** list, I choose the Redshift cluster to see the list of the available recovery points.\n\n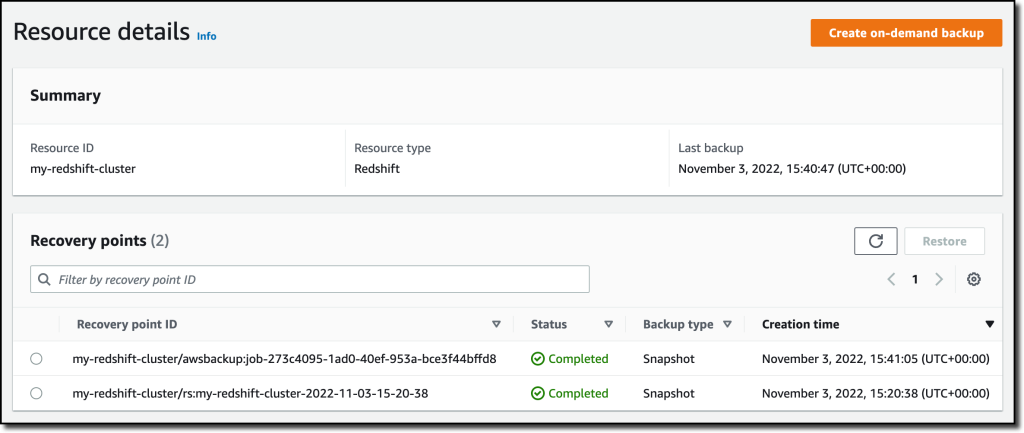\n\nWhen I choose one of the recovery points, I have the option to restore the full data warehouse or just a table into a new Redshift cluster.\n\n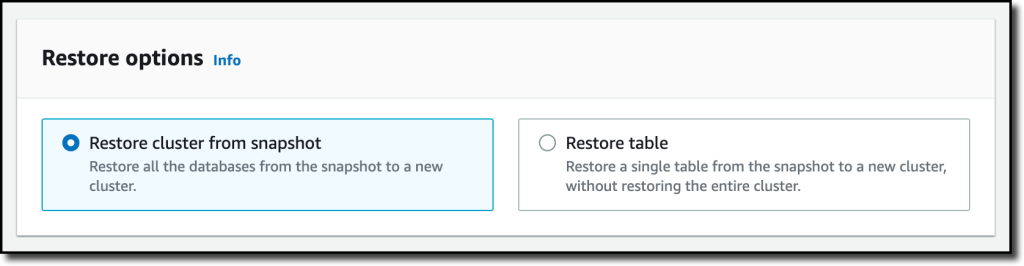\n\nI now have the possibility to edit the cluster and database configuration, including security and networking settings. I just update the cluster identifier, otherwise the restore would fail because it must be unique. Then, I choose Restore backup to start the restore job.\n\nAfter some time, the restore job has completed, and I see the old and the new clusters in the Amazon Redshift console. Using Amazon Web Services Backup gives me a simple centralized way to manage data protection for Redshift clusters as well as many other resources in my Amazon Web Services accounts.\n\n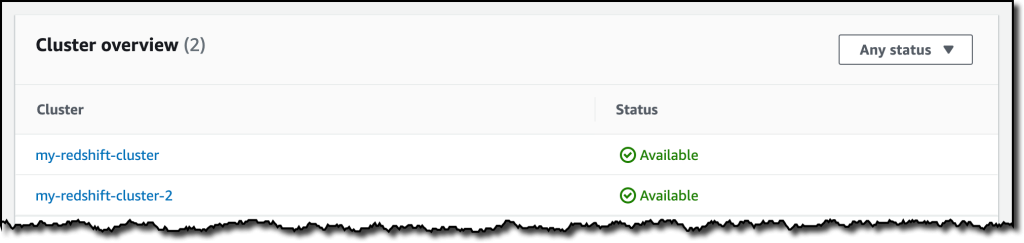\n\n**++Availability and Pricing++**\n[Amazon Redshift](https://aws.amazon.com/redshift/) support in [Amazon Web Services Backup](https://aws.amazon.com/backup/) is available today in the [Amazon Web Services Regions](https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/regions_az/) where both Amazon Web Services Backup and Amazon Redshift are offered, with the exception of the Regions based in China. You can use this capability via the [Amazon Web Services Management Console](https://console.aws.amazon.com/), [Amazon Web Services Command Line Interface (CLI)](https://aws.amazon.com/cli/), and [Amazon Web Services SDKs](https://aws.amazon.com/tools/).\n\nThere is no additional cost for using Amazon Web Services Backup compared to the native snapshot capability of Amazon Redshift. Your overall costs depend on the amount of storage and retention you need. For more information, see [Amazon Web Services Backup pricing](https://aws.amazon.com/backup/pricing/).\n\n— [Danilo](https://twitter.com/danilop)\n\n\n\n### [Danilo Poccia](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/author/danilop/)\n\nDanilo works with startups and companies of any size to support their innovation. In his role as Chief Evangelist (EMEA) at Amazon Web Services, he leverages his experience to help people bring their ideas to life, focusing on serverless architectures and event-driven programming, and on the technical and business impact of machine learning and edge computing. He is the author of Amazon Web Services Lambda in Action from Manning.\n","render":"<p>With <a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/redshift/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Redshift</a>, you can analyze data in the cloud at any scale. Amazon Redshift offers native data protection capabilities to protect your data using automatic and manual snapshots. This works great by itself, but when you’re using other Amazon Web Services services, you have to configure more than one tool to manage your data protection policies.</p>\n<p>To make this easier, I am happy to share that we added support for Amazon Redshift in <a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/backup/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Web Services Backup</a>. Amazon Web Services Backup allows you to define a central backup policy to manage data protection of your applications and can now also protect your Amazon Redshift clusters. In this way, you have a consistent experience when managing data protection across all supported services. If you have a multi-account setup, the centralized policies in Amazon Web Services Backup let you define your data protection policies across all your accounts within your<a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/organizations/\" target=\"_blank\"> Amazon Web Services Organizations</a>. To help you meet your regulatory compliance needs, Amazon Web Services Backup now includes Amazon Redshift in its <a href=\"https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-backup/latest/devguide/aws-backup-audit-manager.html\" target=\"_blank\">auditor-ready reports</a>. You also have the option to use <a href=\"https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-backup/latest/devguide/vault-lock.html\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Web Services Backup Vault Lock</a> to have immutable backups and prevent malicious or inadvertent changes.</p>\n<p>Let’s see how this works in practice.</p>\n<p><strong><ins>Using Amazon Web Services Backup with Amazon Redshift</ins></strong><br />\nThe first step is to turn on the <strong>Redshift</strong> resource type for Amazon Web Services Backup. In the<a href=\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/backup\" target=\"_blank\"> Amazon Web Services Backup console</a>, I choose <strong>Settings <strong>in the navigation pane and then, in the <strong>Service opt-in</strong> section,</strong> Configure resources</strong>. There, I toggle the <strong>Redshift</strong> resource type on and choose <strong>Confirm</strong>.</p>\n<p><img src=\"https://dev-media.amazoncloud.cn/81d73e22ff3648ce9c0f64f39019cf4d_image.png\" alt=\"image.png\" /></p>\n<p>Now, I can create or update a <strong>backup plan</strong> to include the backup of all, or some, of my Redshift clusters. In the backup plan, I can define how often these backups should be taken and for how long they should be kept. For example, I can have daily backups with one week of <strong>retention</strong>, weekly backups with one month of retention, and monthly backups with one year of retention.</p>\n<p>I can also create on-demand backups. Let’s see this with more details. I choose <strong>Protected resources</strong> in the navigation pane and then <strong>Create on-demand backup</strong>.</p>\n<p>I select <strong>Redshift</strong> in the <strong>Resource type</strong> dropdown. In the Cluster identifier, I select one of my clusters. For this workload, I need two weeks of retention. Then, I choose <strong>Create on-demand backup</strong>.</p>\n<p><img src=\"https://dev-media.amazoncloud.cn/106513cf27fc45fa833ae66dfd005dd8_image.png\" alt=\"image.png\" /></p>\n<p>My data warehouse is not huge, so after a few minutes, the backup job has completed.</p>\n<p><img src=\"https://dev-media.amazoncloud.cn/6e8918ddb2e54f13b0831ebfa810367b_image.png\" alt=\"image.png\" /></p>\n<p>I now see my Redshift cluster in the list of the resources protected by Amazon Web Services Backup.</p>\n<p><img src=\"https://dev-media.amazoncloud.cn/05d5409ba67d40bb808121d06206789b_image.png\" alt=\"image.png\" /></p>\n<p>In the <strong>Protected resources</strong> list, I choose the Redshift cluster to see the list of the available recovery points.</p>\n<p><img src=\"https://dev-media.amazoncloud.cn/a60368c6b6d14a8fb415a87168417238_image.png\" alt=\"image.png\" /></p>\n<p>When I choose one of the recovery points, I have the option to restore the full data warehouse or just a table into a new Redshift cluster.</p>\n<p><img src=\"https://dev-media.amazoncloud.cn/2507d6719509456e8212b8f05bb6af14_image.png\" alt=\"image.png\" /></p>\n<p>I now have the possibility to edit the cluster and database configuration, including security and networking settings. I just update the cluster identifier, otherwise the restore would fail because it must be unique. Then, I choose Restore backup to start the restore job.</p>\n<p>After some time, the restore job has completed, and I see the old and the new clusters in the Amazon Redshift console. Using Amazon Web Services Backup gives me a simple centralized way to manage data protection for Redshift clusters as well as many other resources in my Amazon Web Services accounts.</p>\n<p><img src=\"https://dev-media.amazoncloud.cn/302dcd4373ac46678201fe90d08b796d_image.png\" alt=\"image.png\" /></p>\n<p><strong><ins>Availability and Pricing</ins></strong><br />\n<a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/redshift/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Redshift</a> support in <a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/backup/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Web Services Backup</a> is available today in the <a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/regions_az/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Web Services Regions</a> where both Amazon Web Services Backup and Amazon Redshift are offered, with the exception of the Regions based in China. You can use this capability via the <a href=\"https://console.aws.amazon.com/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Web Services Management Console</a>, <a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/cli/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Web Services Command Line Interface (CLI)</a>, and <a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/tools/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Web Services SDKs</a>.</p>\n<p>There is no additional cost for using Amazon Web Services Backup compared to the native snapshot capability of Amazon Redshift. Your overall costs depend on the amount of storage and retention you need. For more information, see <a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/backup/pricing/\" target=\"_blank\">Amazon Web Services Backup pricing</a>.</p>\n<p>— <a href=\"https://twitter.com/danilop\" target=\"_blank\">Danilo</a></p>\n<p><img src=\"https://dev-media.amazoncloud.cn/52a6defa5f7241c4a3966e7c13d47273_danilo%281%29.png\" alt=\"danilo1.png\" /></p>\n<h3><a id=\"Danilo_Pocciahttpsawsamazoncomblogsawsauthordanilop_50\"></a><a href=\"https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/author/danilop/\" target=\"_blank\">Danilo Poccia</a></h3>\n<p>Danilo works with startups and companies of any size to support their innovation. In his role as Chief Evangelist (EMEA) at Amazon Web Services, he leverages his experience to help people bring their ideas to life, focusing on serverless architectures and event-driven programming, and on the technical and business impact of machine learning and edge computing. He is the author of Amazon Web Services Lambda in Action from Manning.</p>\n"}
New – Amazon Redshift Support in Amazon Web Services Backup
海外精选
re:Invent
Amazon Redshift
Amazon Backup
海外精选的内容汇集了全球优质的亚马逊云科技相关技术内容。同时,内容中提到的“AWS”
是 “Amazon Web Services” 的缩写,在此网站不作为商标展示。

 0
0 0
0亚马逊云科技解决方案 基于行业客户应用场景及技术领域的解决方案
联系亚马逊云科技专家
 相关产品
相关产品目录
 相关产品
相关产品亚马逊云科技解决方案 基于行业客户应用场景及技术领域的解决方案
联系亚马逊云科技专家
亚马逊云科技解决方案
基于行业客户应用场景及技术领域的解决方案
联系专家
0
目录
 分享
分享 点赞
点赞 收藏
收藏 目录
目录立即关注

亚马逊云开发者
公众号

User Group
公众号

亚马逊云科技
官方小程序
“AWS” 是 “Amazon Web Services” 的缩写,在此网站不作为商标展示。
立即关注

亚马逊云开发者
公众号

User Group
公众号

亚马逊云科技
官方小程序
“AWS” 是 “Amazon Web Services” 的缩写,在此网站不作为商标展示。
立即关注

亚马逊云开发者
公众号

User Group
公众号

亚马逊云科技
官方小程序
“AWS” 是 “Amazon Web Services” 的缩写,在此网站不作为商标展示。


